Date Palms
The Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) is a palm in the genus Phoenix, extensively cultivated for its edible…

Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Garibaldi (July 4, 1807 - June 2, 1882) was an Italian military and political figure.

Henry George
Henry George (September 2, 1839 - October 29, 1897) was an American political economist and the most…

Chew's House
Benjamin Chew (November 19, 1722 – January 20, 1810) was a fifth-generation American, a Quaker-born…

Handbill Issued by Democratic Party
A political cartoon released by the Democratic Party mocking the Hartford Convention candidate.

Morgan Dix
Morgan Dix (born November 1, 1827 in New York City; died April 29, 1908) was an American priest, "divine"…
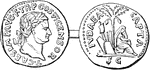
Roman Coins (Denarius)
An illustration of a roman coin (denarius). The left side represents the laurel-crowned head of Titus.…

Crusaders
An illustration of crusaders before Jerusalem. The Crusades were a series of military campaigns of a…

Robert Green Ingersoll
Colonel Robert Green Ingersoll (August 11, 1833 – July 21, 1899) was a Civil War veteran, American…

Isabella of Castille
Isabella I (April 22, 1451 – November 26, 1504) was Queen of Castile and León. She and…
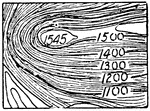
Contour System
In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height)…

Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 1599 Old Style– 3 September 1658 Old Style) was an English military…

Robert Young Hayne
(1791-1839) an American political leader, lawyer, and captain in the War of 1812.

Tammany Hall
Tammany Hall was the Democratic Party political machine that played a major role in controlling New…
Richard Mentor Johnson's Monument
Richard Mentor Johnson (October 17, 1780 or 1781 – November 19, 1850) was the ninth Vice President…

Non Importation Act
Newspapers and speakers especially condemned the "land embargo" — the cutting-off trade with Canada.…

Texas Rangers
The Texas Ranger Division, commonly called the Texas Rangers, is a law enforcement agency with statewide…

Samuel Jones Tilden
Samuel Jones Tilden (February 9, 1814 – August 4, 1886) was the Democratic candidate for the U.S.…

Tippecanoe Battle Ground in 1860
The Battle of Tippecanoe was fought in 1811 between United States forces led by Governor William Henry…

Robert Augustus Toombs
Robert Augustus Toombs (July 2, 1810 – December 15, 1885) was an American political leader, Secretary…

Benjamin Franklin Tracy
Benjamin Franklin Tracy (April 26, 1830 – August 6, 1915) was a United States political figure…
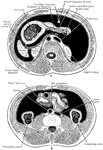
Transverse Section of Abdomen
Diagrammatic transverse section of abdomen, to show the peritoneum on transverse tracing. A, at level…
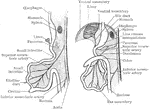
Development of the Intestinal Canal
Two diagrams to illustrate the development of the intestinal canal. The figure to the right shows the…

Henry Laurens
Henry Laurens (March 6, 1724 – December 8, 1792) was an American merchant and rice planter from…

Francis Lieber
Dr. Francis Lieber (March 18, 1800 – October 2, 1872) was a German-American jurist and political philosopher.…

John Alexander Logan
John Alexander Logan (February 8, 1826 – December 26, 1886) was an American soldier and political…

John Davis Long
John Davis Long (October 27, 1838 – August 28, 1915) was a U.S. political figure. He served as Governor…

William Marcy Tweed
William M. Tweed (April 3, 1823 – April 12, 1878), sometimes informally called Boss Tweed, was an…

Seth Low
Seth Low (January 18, 1850 - September 17, 1916), born in Brooklyn, New York, was an American educator…

Coffea Arabica
Coffea arabica is a species of coffee indigenous to Ethiopia and Yemen. It is also known as the "coffee…

Artemas Ward
Artemas Ward (November 26, 1727 – October 28, 1800) was an American major general in the American…

George Edwin Waring
George Edwin Waring was born in Poundridge, NY, July 4, 1833. He was agricultural engineer of Central…
Date Palm Leaf
An illustration of a portion of a date palm leaf. The Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) is a palm in the…
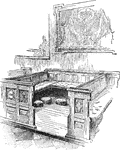
Washington's Pew at St. Paul's, New York
In some churches, pews were installed at the expense of the congregants, and were their personal property;…

Dracaena
Dracaena is a genus of about 40 species of trees and succulent shrubs classified in the family Ruscaceae…

Earthworm
An illustration of an earthworm. The basic body plan of an earthworm is a tube, the digestive system,…
Tracheal System of Fly Larva
Tracheal system of a fly larva. Labels: Tr, longitudinal stem of right side; St', St", anterior and…
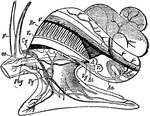
Circulatory and Nervous System of a Snail
Circulatory and nervous system of a snail. Labels: F, tentacles; Oe, esophagus; Cg, cerebral ganglion;…
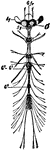
Circulatory System of an Annelid
Anterior part of the circulatory system of an annelid. The arrows indicate the direction of the flow.…
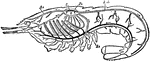
Circulatory and Respiratory System of a Crayfish
Circulatory and respiratory system of the crayfish. C-heart with three pairs of ostia; Ps, pericardium;…
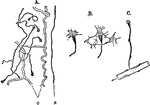
Protonephridium
Structure of the protonephridium (excretory organ) of a flatworm. A, part of the excretory apparatus…
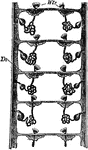
Protonephridium of an Annelid
Structure of the protonephridium (excretory organ) of an annelid. Labels: Wtr, ciliated funnels; Ds,…

Protonephridium of a Shark
Structure of the protonephridium (excretory organ) of a shark. Labels: Wtr, ciliated funnels; Ug, segmental…
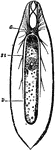
Nervous System of the Flatworm
Nervous system of a flatworm. Labels: G, cerebral ganglia and eyes; St, the two lateral nerve trunks;…
Nervous System of a Ladybug Larva
Nervous system of the larva of a ladybug. Labels: Gfr, frontal ganglion; G, cerebral ganglia; Sg, subcesophageal…
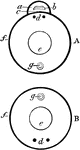
Vertebrate and Invertebrate
A, Diagrammatic transverse section through the body of a vertebrate. B, A similar section through a…

Lachlan McIntosh
Lachlan McIntosh (March 17, 1725 – February 20, 1806) was an American military and political leader…

Samuel Finley Breese Morse
Samuel Finley Breese Morse (April 27, 1791 – April 2, 1872) was an American painter of portraits…

A Wasp on a Frolic
A caricature celebrating the victory of the USS Wasp over the HMS Frolic and the accompanying…

Canada Thistle
Cirsium arvense is a species of Cirsium, native throughout Europe and northern Asia, and widely introduced…

Marinus Willett
Marinus Willett (July 31, 1740 – August 22, 1830) was an American soldier and political leader from…

Political Cartoon about Oliver Hazard Perry
A political cartoon discussing Commodore Oliver Hazard Perry, an officer in the United States Navy.
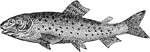
Brook Trout
The brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis, (sometimes called the eastern brook trout, Adirondack coaster…

John Winthrop
John Winthrop (12 January 1588 – 26 March 1649) led a group of English Puritans to the New World,…

Order of the Garter Star
An illustration of the Order of the Garter Star. The Most Noble Order of the Garter is an order of chivalry,…

Sea Fern Fossil
An illustration of a sea fern fossil from the carboniferous period. The Carboniferous is a geologic…

Fernando Wood
Fernando Wood (June 14, 1812 – February 14, 1881) is famous for being one of the most colorful mayors…

Josiah Quincy
Josiah Quincy III (February 4, 1772 – July 1, 1864) was a U.S. educator and political figure. He was…